Stainless Steel 440C
MIM 440C Introduction
MIM 440C is a martensitic stainless steel, this stainless steel has excellent strength, hardness, and wear resistance. This 440C stainless steel is suitable for application with high strength, hardness, wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
Stainless steel 440C is the hardest steel materials, it is the martensitic stainless steel with high carbon content and chromium content. Its wide applications including: surgical tools, dental instruments, cutting inserts, bearings, pumps and valves.
Chemical Composition
The common composition of MIM 440C after sintering is as following:
| Stainless steel 440C | Iron | Silicon | Carbon | Chromium | Manganese | Molybdenum |
| Percent by Weight | BaL. | 1.00 | 0.95-1.2 | 16.00-18.00 | 1.00 | 0.75 |
Typical Mechanical Properties
The typical mechanical properties of MIM 440C are as following:
| Material | Density | Tensile Strength | Yield Strength(0.2%) | ImpactStrength | Hardness | Elongation(% in 25.4mm) |
| Stainless steel 440C | ≥7.5g/cm³ | ≥700Mpa | ≥600Mpa | 115J | 30-39 HRC | ≥1% |
Stainless Steel 440C Properties
Corrosion Resistance
Stainless steel 440C has good resistance to the atmosphere, water, foods, alkalies and mild acids. The best resistance can achieve in the post-treatment of hardening, tempering, and passivization. In most conditions, SS 440C has approximate corrosion resistance grade as SS304.
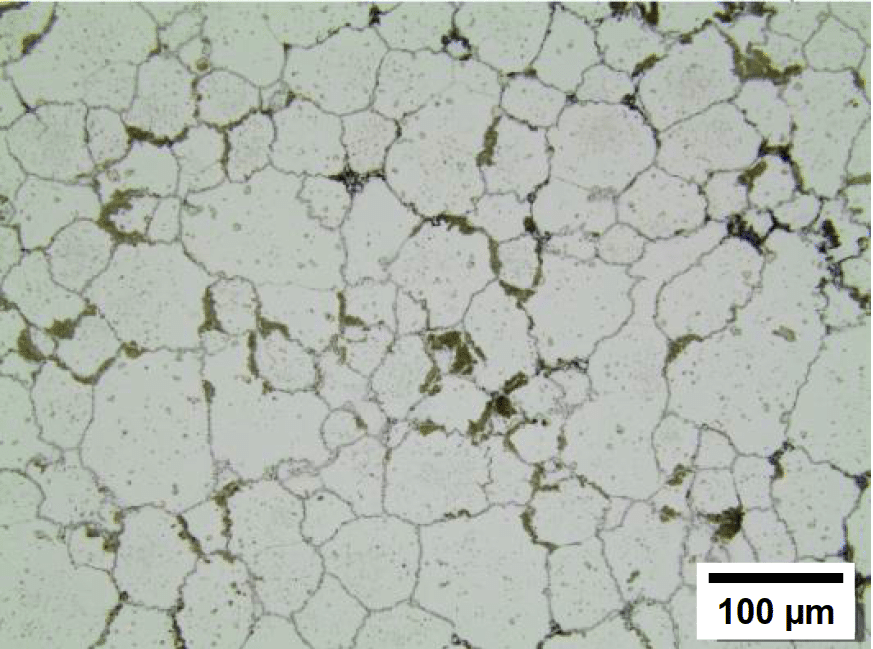

SEM of 440C sintered
Heat Resistance
As the over-tempering will reduce overall mechanical properties of stainless steel 440C, we don’t recommend applying these parts over the relevant tempering temperatures.
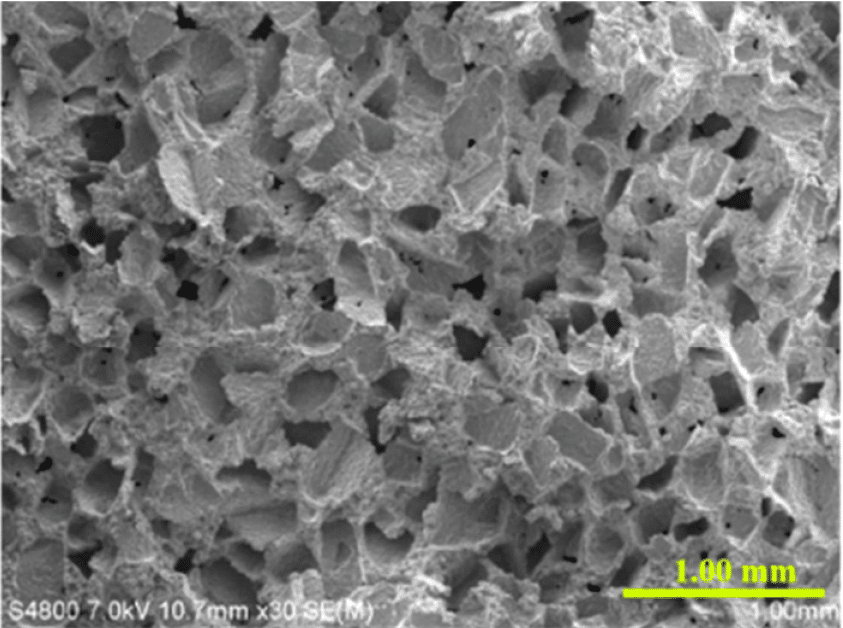
SEM image of SS 440C internal pore
MIM 440C Post-Processing
Annealing
Full anneal at 850-900 °C, then slow furnace cool to 600 °C. While sub-critical annealing at 735-785°C and slow furnace cool.
Hardening
Quenching in warm oil or air after heat to 1010-1065 °C, in order to obtain different hardness values.
Tempering
Tempering in 425-565°C will reduce impact and corrosion resistance, and tempering in 590-675°C results in low hardness and high impact resistance.
Machining
Similar as high speed steel, the annealed 440C is easily machined. After hardening process, it is more difficult to machine.
Stainless Steel 440C in MIM Technology
Because of high difficulty in machining, most stainless steel parts are produced by precision casting. Otherwise, the limitation of design geometry and other defects will result in unsatisfactory tolerance and surface roughness. Therefore, metal injection molding (MIM) is the most suitable fabrication technology for stainless parts. It can make complex parts with excellent properties at low price.
However, in reason of technical difficulties, there are few MIM manufacturers can apply MIM technology for 440C materials. ZCMIM has concentrated in the research of MIM 440C debinding and sintering, and successfully produced different MIM 440C part
MIM Process Parameters on 440C Properties
Metal injection molding technology can manufacture the high-strength and high-hardness of stainless steel 440C. Otherwise, different process parameters in MIM process will result in significant alternation in final mechanical properties and micro-structures. In MIM 440C process, there are three key parameters: sintering atmosphere & temperature, powder loading, carbon addition.
Sintering Atmosphere & Temperature
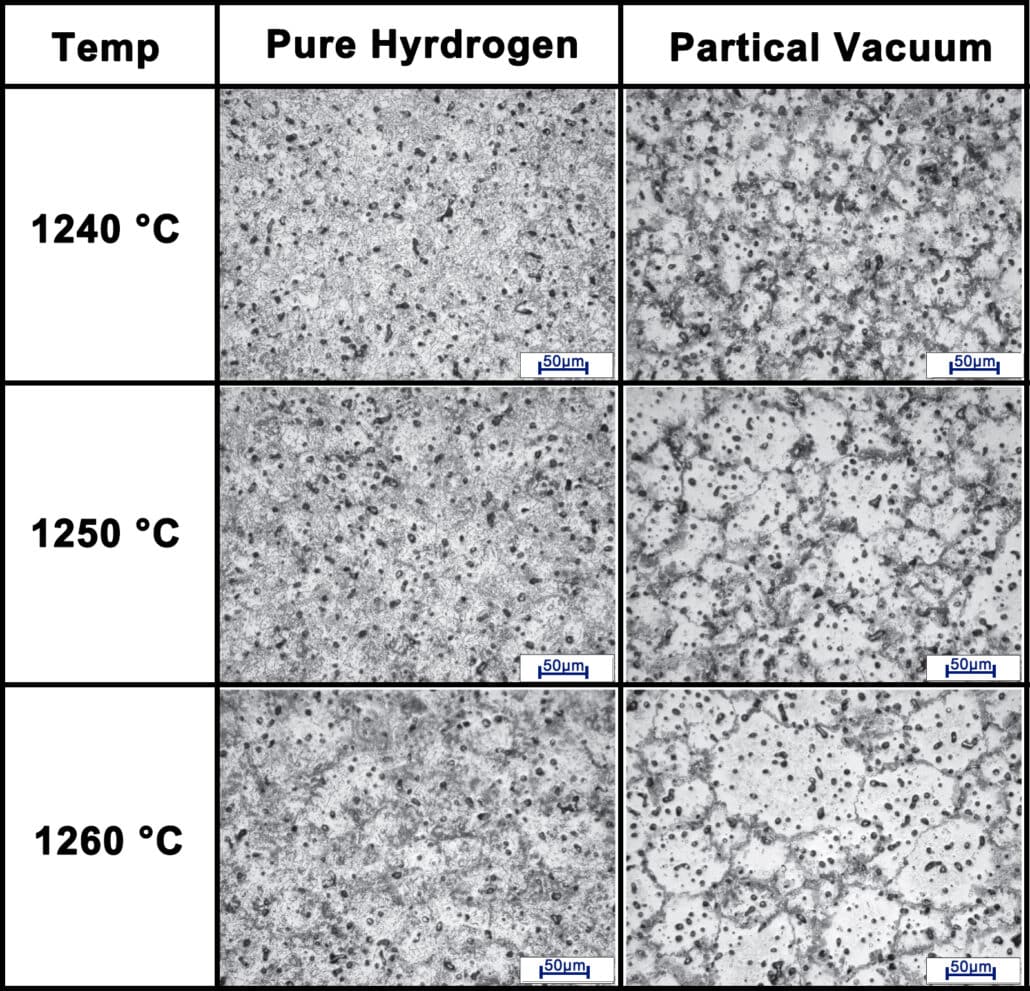
Normally, the higher sintering temperatures give rise to slight higher densities of sintered 440C parts in both pure hydrogen and partical vaccum atmospheres. In addition, the parts sintered in pure hydrogen is also denser than that in partial vacuum atmosphere. From the following optical micro-structures of sintered 440C parts at different sintering temperature. Although higher temperature sintering attain higher densification stage, there are still continuous carbide network on micro-structure.
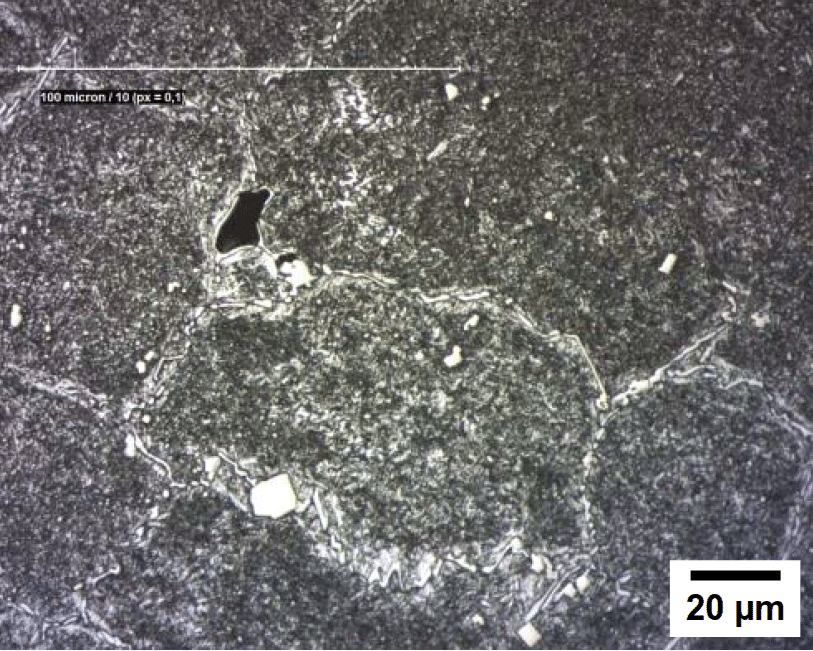
After heat treatment, the morphology of 440C matrix is composing of martensitic phase, finely primary carbide distribution, secondary carbide network, and retain austenite phase. We can find the micro-structure in the following picture.
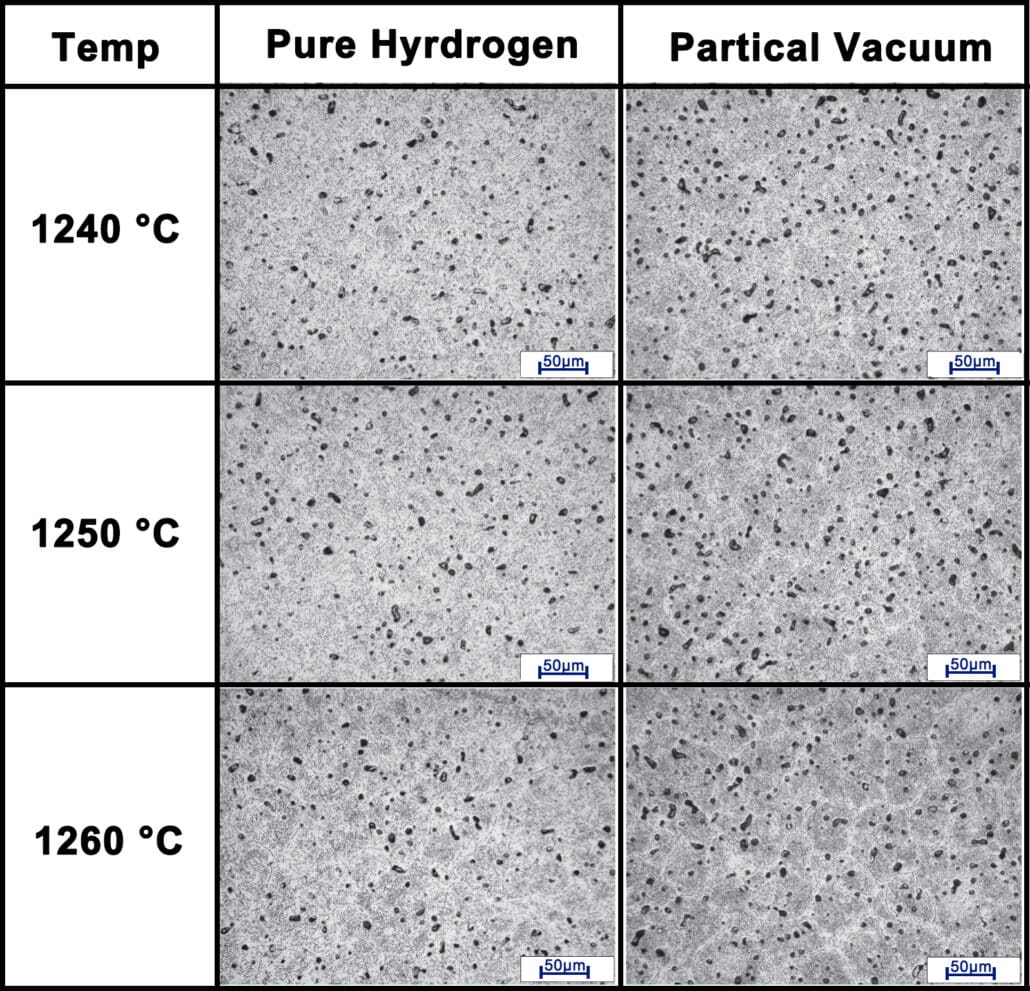

In addition, the hardness of 440C parts increase at least 50% after heat treatment. Comparatively, the SS 440C parts achieve lower performance in pure hydrogen than in partial vacuum.
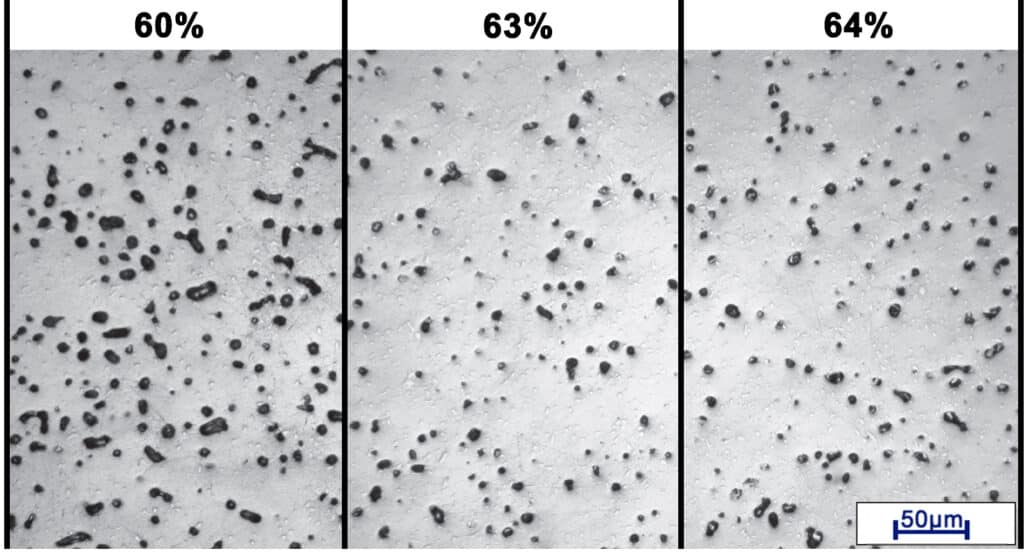
Powder Loading
In the following picture, high powder loading of 64% will increase the density simply. Sine there is lesser space between metal powder particles to be densified during MIM sintering process.
Carbon Addition
Since the high oxygen concentration in the initial powders, the average loss of carbon concentration for sintered parts is approximate 0.25 %. Carbon addition can anticipate and compensate this amount of loss. Once add 0.4% of activated carbon powder(ACP) to base 440C powders, the final sintering density will increase 2.5%, and final hardness can reach to as high as 63 HRC.
Conclusion
Stainless steel 440C is the martensitic stainless steel for high level of mechanical properties. ZCMIM applies metal injection molding (MIM) technology to manufacture excellent 440C parts in a cost-effective way. Contact us for your new MIM 440 project.